Housing, Infrastructure and Communities Canada ‑ Quarterly Financial Report for the Quarter Ended December 31, 2024
Pursuant to the Royal Assent of Bill C-59 and effective June 20, 2024, Infrastructure Canada (INFC) became Housing, Infrastructure and Communities Canada (HICC). The 2024-25 Q3 Quarterly Financial Report (QFR) is the second reported under HICC.
Statement outlining results, risks and significant changes in operations, personnel and programs
Introduction
This quarterly report has been prepared by management as required by Section 65.1 of the Financial Administration Act and in the form and manner prescribed by the Treasury Board. This quarterly report should be read in conjunction with Supplementary Estimates B.
The key to building Canada for the 21st century is helping all communities thrive by making housing more available and affordable while making public infrastructure more sustainable, inclusive and climate-resilient. HICC makes significant investments in housing and public infrastructure, addresses homelessness needs, builds public-private-partnerships, and delivers programs that improve Canadians' quality of life while creating jobs and supporting economic growth.
Further information on HICC’s mandate, responsibilities, and programs can be found on HICC’s Website.
Basis of Presentation
This quarterly report has been prepared by management using an expenditure basis of accounting. The accompanying Statement of Authorities includes HICC’s spending authorities granted by Parliament and those used by HICC consistent with the Main Estimates and Supplementary Estimates for the 2024-25 fiscal year (FY). This quarterly report has been prepared using a special purpose financial reporting framework designed to meet financial information needs with respect to the use of spending authorities.
The authority of Parliament is required before monies can be spent by the government. Approvals are given in the form of annually approved limits through Appropriation Acts or through legislation in the form of statutory spending authority for specific purposes.
HICC uses the full accrual method of accounting to prepare and present its annual departmental financial statements that are part of the departmental performance reporting process. However, the spending authorities voted by Parliament remain on an expenditure basis.
HICC works in collaboration with other federal departments and agencies to deliver some of its transfer payment programs (collectively known as federal delivery partners).
It should be noted that this quarterly report has not been subject to an external audit or review.
Highlights of Fiscal Quarter and Fiscal Year-to-Date Results
HICC was created on June 20, 2024, therefore no historical comparative data is presented. Historical data is being retained beginning the second quarter of fiscal year 2024-25 and will provide a comparative for the 2025-26 fiscal year.
This section presents HICC’s available authorities as of the third quarter of fiscal year 2024-25. Any unspent appropriations by INFC (Vote 1, 5, and 10) have been deemed appropriated to HICC. This QFR reports expenditures recorded under authorities appropriated to HICC for the quarter ending December 31, 2024.
Authorities
Graph 1: Authorities Available as of December 31, 2024
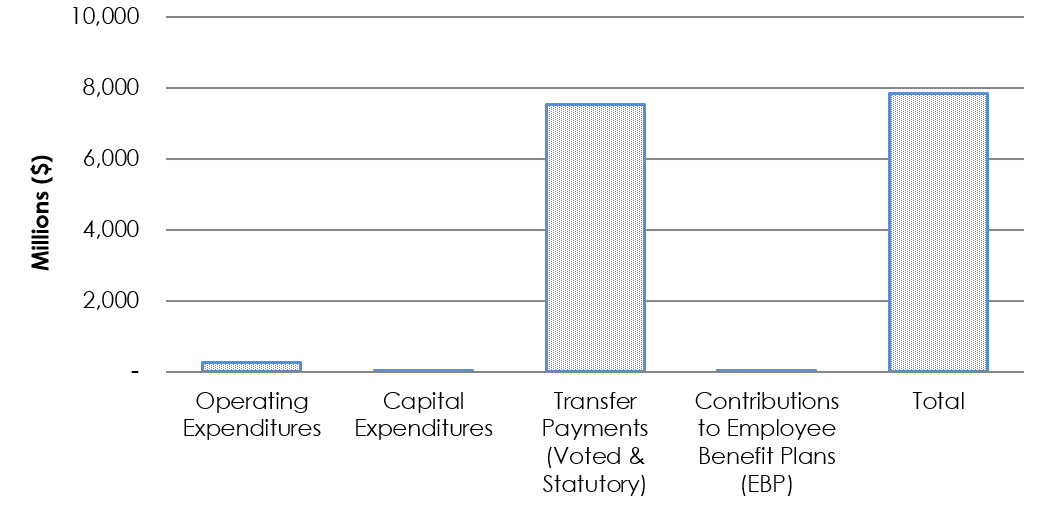
Text description of Graph 1
Graph 1: Authorities Available as of December 31, 2024.
Bar graph showing the authorities available for use as of December 31, 2024.
- Operating authorities available as of Q3 2024-25 were $261.8 million.
- Capital authorities available as of Q3 2024-25 were $36.8 million.
- Transfer Payment (Voted and Statutory) authorities available as of Q3 2024-25 were $7.5 billion.
- Contributions to the Employee Benefit Plan authorities available as of Q3 2024-25 were $16.5 million.
- The total of authorities available for use as of Q3 2024-25 were $7.8 billion.
As shown in the Statement of Authorities, HICC’s total authorities available for 2024-25 are $7.8 billion as of the end of the third quarter (Q3).
HICC’s available authorities are summarized in the table below:
| Authorities |
Available Amount (000’s) |
|---|---|
|
Operating Expenditures |
261,773 |
|
Capital Expenditures |
36,781 |
|
Transfer Payments (Voted and Statutory) |
7,517,206 |
|
Contributions to Employee Benefit Plans (EBP) |
16,513 |
Expenditure Analysis
HICC year-to-date expenditures (from June 21, 2024 to the end of the third quarter) represent $3.3 billion. Total expenditures by type are summarized in the graphs and tables below.
Graph 2: Total Expenditures as of December 31, 2024
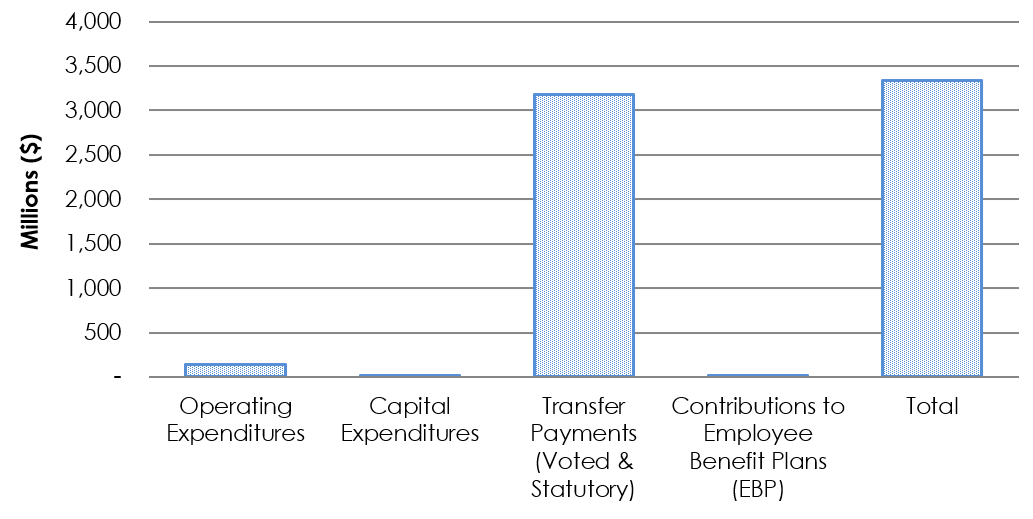
Text description of Graph 2
Graph 2: Total Expenditures as of December 31, 2024.
Bar graph showing the total expenditures used year-to-date as of December 31, 2024.
- Authorities used for Operating as of Q3 2024-25 were $145.8 million.
- Authorities used for Capital as of Q3 2024-25 were $4.6 million.
- Authorities used for Transfer Payments (Voted and Statutory) as of Q3 2024-25 were $3.2 billion.
- Authorities used for Contributions to the Employee Benefit Plan as of Q3 2024-25 were $9.6 million.
- Total year-to-date budgetary expenditures as of Q3 2024-25 were $3.3 billion.
| Year-to-date expenditures |
Amount Spent (000’s) |
|---|---|
|
Operating Expenditures |
145,771 |
|
Capital Expenditures |
4,567 |
|
Transfer Payments (Voted and Statutory) |
3,179,771 |
|
Contributions to Employee Benefit Plans |
9,606 |
Graph 3: Authorities used for Transfer Payments (Voted and Statutory) as of December 31, 2024
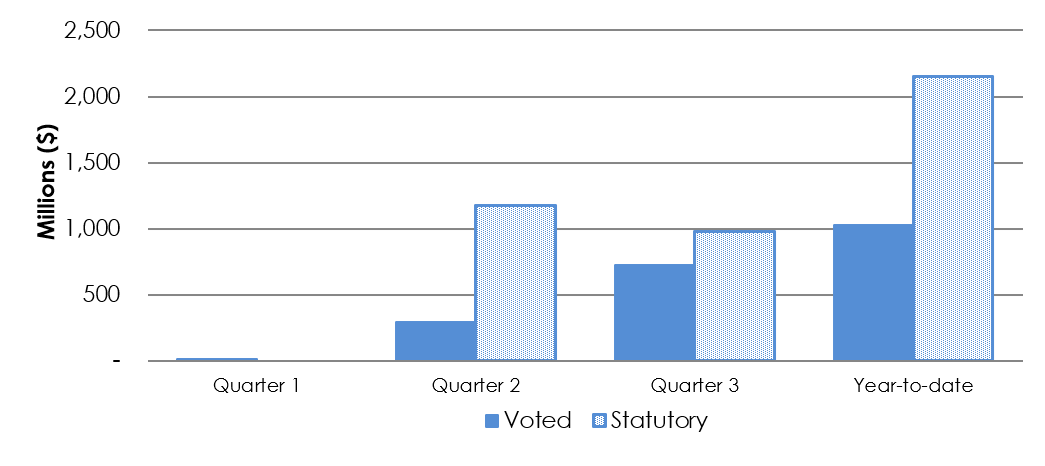
Text description of Graph 3
Graph 3: Authorities used for Transfer Payments (Voted and Statutory) as of December 31, 2024.
Bar graph showing the authorities used for Transfer Payment (Voted) and Transfer Payments (Statutory) as of December 31, 2024.
- Voted transfer payments expensed as of Q3 2024-25 were $1.0 billion.
- Statutory transfer payments expensed as of Q3 2024-25 were $2.2 billion.
Significant year-to-date transfer payment expenditures as of December 31, 2024 were as follows:
| Program Fund | Amount Spent (000’s) |
|---|---|
| Canada Community-Building Fund* | 2,151,518 |
New Building Canada Fund-Provincial-Territorial Infrastructure Component-National and Regional Projects |
181,370 |
Green & Inclusive Community Buildings |
158,526 |
Investing in Canada Infrastructure Program – Public Transit Infrastructure Stream |
154,415 |
Investing in Canada Infrastructure Program – Green Infrastructure Stream |
108,683 |
Reaching Home: Canada's Homelessness Strategy |
82,776 |
Investing in Canada Infrastructure Program - Rural & Northern Infrastructure Stream |
68,206 |
Disaster Mitigation and Adaptation Fund |
50,553 |
Investing in Canada Infrastructure Program - COVID 19 Resilience Stream |
47,160 |
Investing in Canada Infrastructure Program - Community, Culture, & Recreation Stream |
42,847 |
* Canada Community-Building Fund is HICC’s only Statutory program.
Departmental Budgetary Expenditures by Standard Object
The planned Departmental Budgetary Expenditures by Standard Object are set out in the table at the end of this report. As mentioned above, year-to-date expenditures as of Q3 2024-25 were $3.3 billion. The largest single factor was transfer payments as detailed in Table 3 above.
Year-to-date expenditures by standard object are summarized in the table below:
| Expenditures by Standard Object | Amount Spent (000’s) |
|---|---|
|
Personnel |
106,169 |
|
Transportation and communications |
854 |
|
Information |
2,429 |
|
Professional and special services |
13,496 |
|
Rentals |
1,096 |
|
Repair and maintenance |
10,362 |
|
Utilities, materials and supplies |
91 |
|
Acquisition of land, buildings and works |
3,978 |
|
Acquisition of machinery and equipment |
454 |
|
Transfer payments |
3,179,771 |
|
Public debt charges |
20,910 |
|
Other subsidies and payments |
104 |
Overall, HICC has spent 43% of its current Total Authorities as of December 31, 2024. This is mainly due to the late materialization of Transfer Payments. The majority of HICC G&C spending typically occurs in the final quarter of the fiscal year. The influx of claims submitted for reimbursement at year-end is driven by several factors, including the timing of construction seasons, which has a direct impact on the finalization of claims.
Other material expenditures for HICC include:
- personnel expenditures representing employee wages;
- public debt charges due to interest payments for the Samuel De Champlain Bridge Corridor (SDCBC) project.
- professional and special services such as consultant fees (engineering, management & IT) as well as Memorandums of Understanding (MOUs) with Other Government Departments (OGDs).
Risks and Uncertainties
As part of its corporate risk management function, the Department is monitoring and identifying strategic and department-wide risks that may affect the delivery of its mandate and expected results. HICC integrates risk management principles into strategic business planning, results-based management, decision-making and organizational processes to support the achievement of departmental priorities. Risk management at HICC is carried out in accordance with the Treasury Board Secretariat’s (TBS) Framework for the Management of Risk and TBS’s Guide to Integrated Risk Management.
The Corporate Risk Profile (CRP) is an important component of risk management as it is the primary document that describes the key risk information that should be considered in organizational planning, decision-making and the achievement of departmental priorities. This document also serves as a cornerstone for implementing and monitoring risk responses to effectively address risks that could impede the success of HICC’s priorities. HICC is to update its CRP yearly and revise it every three years or when warranted as a result of significant changes in risk to the Department. This may include significant changes in mandate, changes to priorities and departmental direction, operational objectives, and other factors such as changing economic, political and environmental conditions that directly impact the Department.
The Department is currently developing its 2025-28 CRP, which is expected to be completed in Q4 2024-25. The new CRP will investigate whether there are any important financial risks to be managed considering the ambitious plan for the Department to develop, implement, and deliver on the new and renewed programming that was announced in Budget 2024.
Significant Changes in Relation to Operations, Personnel and Programs
Since the last Quarterly Financial Report (QFR), the following significant changes have taken place within the department:
- The Honourable Nathaniel Erskine-Smith was appointed Minister of Housing, Infrastructure and Communities, effective December 20, 2024, replacing former Minister Sean Fraser.
- Deputy Minister Paul Halucha was appointed Deputy Minister of Housing, Infrastructure and Communities Canada, effective December 31, 2024, replacing former Deputy Minister Kelly Gillis, who retired from the Public Service.
Additionally, pursuant to Budget 2024, the Department secured funding for the following initiatives:
- Funding from the Central Advertising Fund: $9 million over two years beginning in 2024-25.
- Funding to renew the High Frequency Rail Initiative Team: $3 million for 2024-25.
- Funding to maintain stability for Reaching Home: Canada’s Homelessness Strategy: $1 billion over four years beginning in 2024-25.
- Funding to oversee the acquisition of the Quebec Bridge: $7 million over three years beginning in 2025-26.
- Funding for the oversight of the Samuel De Champlain Bridge Corridor (SDCBC) project: $76 million over five years beginning in 2025-26.
- Funding to Modernize and Enhance the Collection and Dissemination of Housing Data: $1 million over four years beginning in 2024-25.
To deliver the new programming in a timely way, it is essential that HICC continue its efforts to attract and recruit employees through adaptable and innovative talent sourcing strategies and retain employees by investing in their professional development to meet business requirements, all while focusing on employee well-being. Initiatives to create an inclusive and barrier-free workplace will continue to be supported in order to ensure HICC remains a workplace of choice, made up of a workforce that is representative of the Canadians we serve.
The role and profile of the Department has grown over the last few years and Budget 2024 positions it well to deliver on the expanded and integrated portfolio. In the face of evolving challenges and growing housing needs, the mandate to design meaningful policies and provide communities with the tools they require to access HICC programs has never been more crucial.
The Department is committed to moving forward on the Budget 2024 measures referenced above in a timely manner as well as those in which it will play a collaborative role, in an effort to deliver results for Canadians.
Approval by Senior Officials
Approved by:
Paul Halucha
Deputy Head
Signed at Ottawa, Canada
Michelle Baron
Chief Financial Officer
Annex A
Quarterly Financial Report
For the quarter ended December 31, 2024
Departmental budgetary expenditures by Standard Objects (unaudited)
(in thousands of dollars)
Fiscal year 2024-25
| Expenditures | Planned expenditures for the year ending March 31, 2025 |
Expended during the quarter ended December 31, 2024 |
Year-to-date used at quarter-end |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Personnel |
140,422 |
47,432 |
106,169 |
|
Transportation and communications |
8,592 |
513 |
854 |
|
Information |
1,212 |
892 |
2,429 |
|
Professional and special services |
74,452 |
7,041 |
13,496 |
|
Rentals |
3,219 |
537 |
1,096 |
|
Repair and maintenance |
20,675 |
5,091 |
10,362 |
|
Utilities, materials and supplies |
209 |
57 |
91 |
|
Acquisition of land, buildings and works |
12,964 |
2,003 |
3,978 |
|
Acquisition of machinery and equipment |
11,444 |
416 |
454 |
|
Transfer payments |
7,517,206 |
1,704,607 |
3,179,771 |
|
Public debt charges |
41,921 |
10,441 |
20,910 |
|
Other subsidies and payments* |
-42 |
92 |
104 |
| Total net budgetary expenditures | 7,832,272 |
1,779,122 |
3,339,715 |
* Negative amount under Standard Object (SO) 12 is due to timing of a transactional adjustment. This adjustment was made after the Royal Assent of Bill C-59 and therefore is only represented in HICC’s books. In reality, the planned expenditures under SO 12 are zero for Fiscal Year 2024-25.
Download
If the following document is not accessible to you, please contact info@infc.gc.ca for assistance.
Statement of Authorities (unaudited)
(in thousands of dollars)
Fiscal year 2024-25
Total available for use for the year ending |
Used during the quarter ended |
Year-to-date used at quarter-end |
||
Vote 1 |
Operating expenditures | 261,682 |
67,201 |
145,708 |
Vote 5 |
Capital expenditures | 36,781 |
2,494 |
4,567 |
Vote 10 |
Contributions | 5,149,048 |
728,167 |
1,028,253 |
| Budgetary Statutory Authorities | ||||
(S) |
Contributions to employee benefit plans | 16,513 |
4,798 |
9,606 |
(S) |
Canada Community-Building Fund | 2,368,158 |
976,439 |
2,151,518 |
(S) |
Minister salary and car allowance | 90 |
22 |
63 |
| Total Budgetary Authorities | 7,832,272 |
1,779,122 |
3,339,715 |
|
| Non-Budgetary Authorities | - |
- |
- |
|
| Total Authorities | 7,832,272 |
1,779,122 |
3,339,715 |
|
Download
If the following document is not accessible to you, please contact info@infc.gc.ca for assistance.
- Statement of Authorities (PDF version) (65.97 KB)
Report a problem on this page
- Date modified:
